Novel plasma state and acceleration of particles achieved by multidiscipline fusion
Project Gist
A new plasma physics based on multidisciplinary research
Keywords
Nanomaterials processing, Chiral materials, High energy density plasma, high intensity laser
Background and Purpose
Nonlinear phenomena are generally observed in various fields such as astrophysics, plasma physics, chemistry, and materials science. In this project, we studied the high-energy-density plasmas formed by irradiation of high-power lasers on sophisticated target materials: nanometric helical objects aligned on a substrate surface prepared by self-organization. All the issues such as the fabrication of the target materials, experiments of high-power laser irradiation, and their simulations are studied based on nonlinear science, through which we tried to develop a new scientific field triggered by multidisciplinary research.
Project Achievements
We succeeded in the production of metallic nanohelices by electrochemical surface processing based on dynamic self-organization, which can serve as the target material for the irradiation of high-power laser. Besides, high-power laser irradiation experiments were successfully carried out using a Si nanorod array which is assumed to be a pseudo array of metallic nanohelices. These experiments gave several new results in view of the physics of high-energy-density plasmas. In the project, we carried out international and multidisciplinary research for the fabrication of metallic nanohelices with colleagues in University of Bordeaux. This activity further strengthens the relationship between Kyoto University and University of Bordeaux.
Future Prospects
As the result of the present project, precise control in the shape of metallic nanohelices has been achieved. Currently, we are working on the control of the alignment of metallic nanohelices standing on a substrate in a highly ordered manner. The achievement of the fabrication of a metallic nanohelix array will give interesting behaviors of high-energy-density plasmas caused by the unique helical structure.
Figure
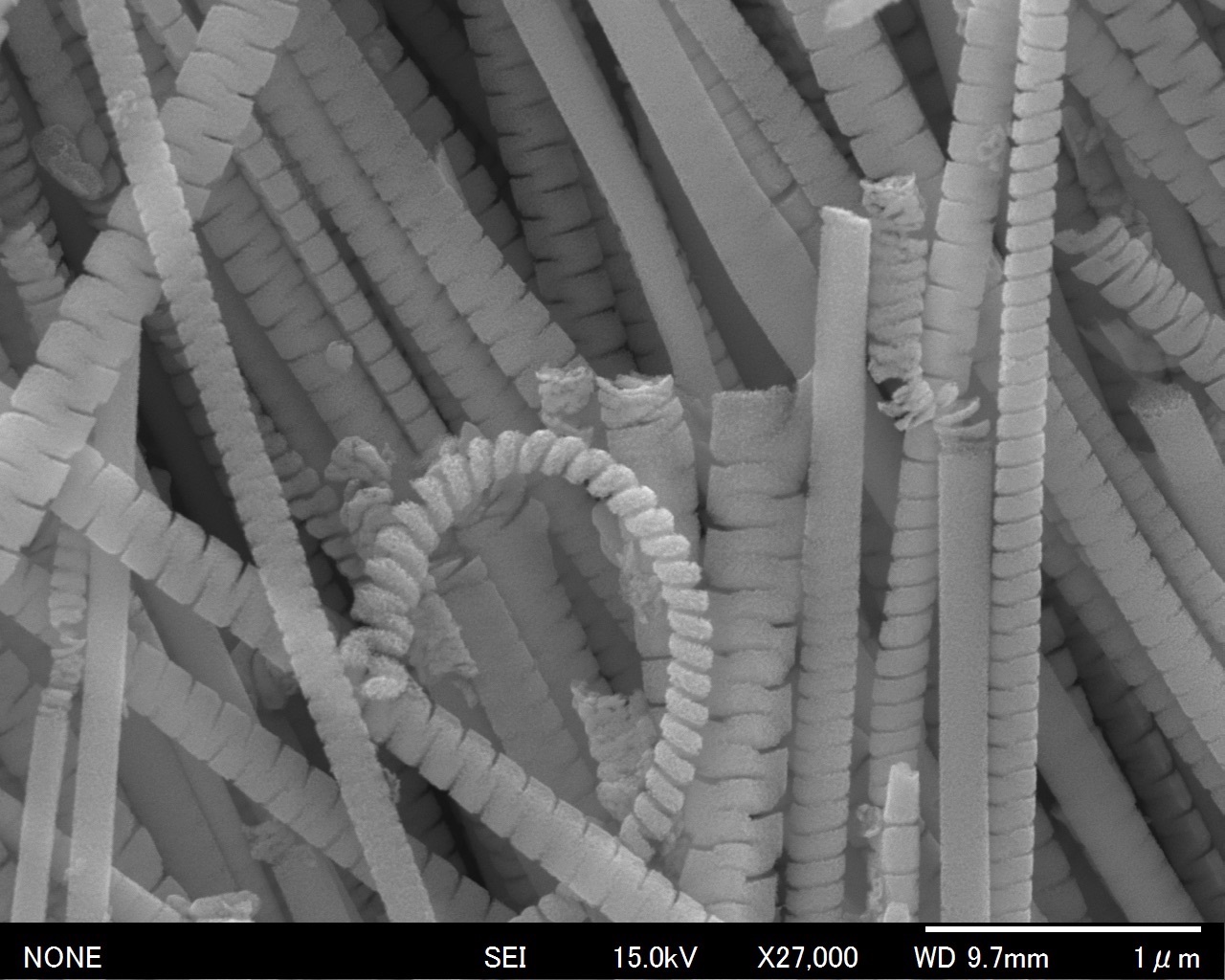

surface processing
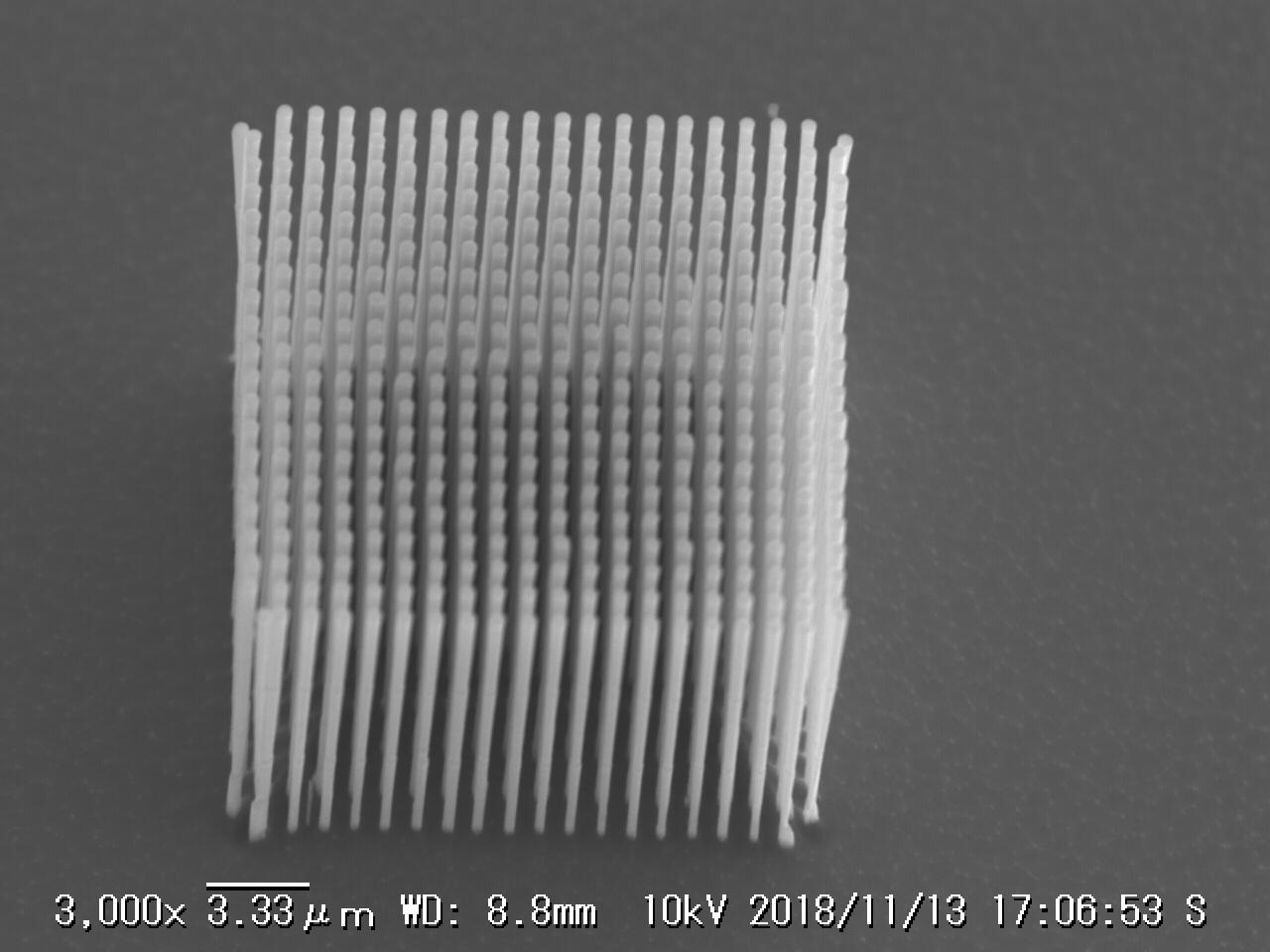
laser irradiation
Principal Investigator

FUKAMI Kazuhiro
Graduate School of Engineering
He received PhD in 2006 from Osaka University. In 2006 he joined Institute of Advanced Energy at Kyoto University as an Assistant Professor, and became an Associate Professor in 2013 at Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Kyoto University. His current research interests include electrochemistry and nonlinear science.
http://www.echem.mtl.kyoto-u.ac.jp/index_fukami.html
