International Joint Research on Bio-CCUS for Realization of Carbon Neutrality
Project Gist
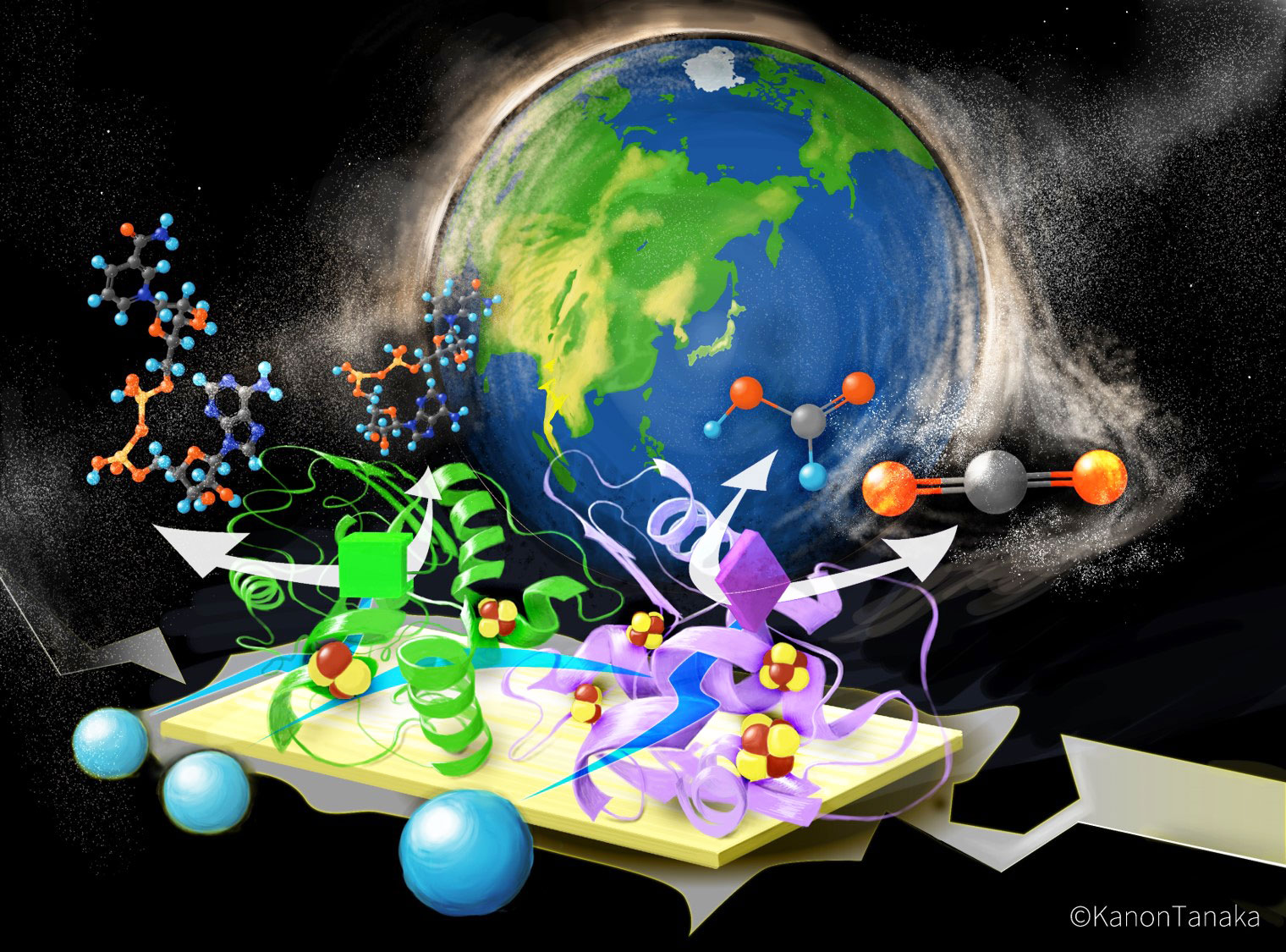
Realizing carbon neutrality with superior biocatalysts
Keywords
CO2 reductase, Carbon dioxide capture and utilization, Redox enzyme, Electron transfer
Background and Purpose
Technology to capture, store, and utilize carbon dioxide (CCUS) is needed around the world to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050. We hope to contribute to the realization of a sustainable world by focusing on advanced biocatalytic functions created by nature. In this research, we aim to create a “bio-CCU” characterized by the direct utilization of CO2 into resources from the atmosphere by utilizing redox enzymes (CO2 reductases) that can efficiently convert CO2 into resources under mild conditions.
Project Achievements
We promoted international collaboration with research groups at CNRS, a national research institute in France, to realize a bio-CCU. In addition to young researchers representing each other, doctoral and master’s students, who will lead the next generation of each group, participated in this project to form a network for innovative research. We succeeded in elucidating the steric structure and reaction mechanism of a key enzyme for bio-CCU, which was accepted for publication in the Outside Front Cover of an international journal (ChemComm) and published in a press release from Kyoto University.
Future Prospects
We would like to contribute to carbon neutrality by utilizing the advanced functions of superior biocatalysts, and would like to further accelerate international joint research for social implementation by combining the wisdom of research groups in Japan and France.
Figure
Principal Investigator

SOWA Keisei
Division of Applied Life Sciences, Graduate School of Agriculture
Keisei Sowa is an assistant professor at Kyoto University. Since he took the position in January 2021, he aims to understand the essence of key functions of living organisms (respiration, metabolisms, and photosynthesis) from the viewpoint of bioelectrochemistry and to contribute to society through biomimetic technology.
Related URL: http://www.bapc.kais.kyoto-u.ac.jp/
